1, ash test

Muffle furnace
Ash: When burning at high temperatures, the polymer undergoes a series of physical and chemical changes. Finally, the organic components volatilize and the inorganic components (mainly inorganic salts and oxides) remain. These residues are called ash. In general modified products, ash is some inorganic minerals such as silica, calcium carbonate, talc, glass fiber and titanium dioxide.
Test method: calcination method (combustion of organic matter and treatment of its residue at a high temperature until constant weight), burning in a muffle furnace at 600 ° C for 10 minutes, weighing the residue.
Ash is expressed in mass percent: (M1-M0)×100/M
M indicates the weight of the model, the weight of the M1 ash and the weight of the cup, and the weight of the M0 cup.
OBJECTIVE: To determine the content of inorganic substances in plastics as a basis for judging the authenticity of materials and as a basis for judging the properties of materials. For example, in plastics with glass fiber, the rigidity of plastic materials is increased, heat resistance is increased, but toughness Lower, on the contrary, the toughness increases and the rigidity heat resistance decreases.
2, moisture test

Infrared moisture tester
Moisture: Refers to the water contained inside the object.
Test principle: Mainly divided into: infrared fast moisture measurement and halogen rapid moisture determination
Infrared moisture test principle: Infrared heating method weight loss is the use of infrared heating object's thermal effect and strong penetration ability, the measured object's moisture quickly evaporates and lose weight, through the initial mass of the object and the mass of the object after evaporation of the water, the measured The water content of an object at a particular temperature.
Halogen rapid moisture determination:
The calculation formula of the test: Let G be the weight before the sample is dried, g be the weight of the sample after drying; L is the moisture content of the sample, R is the sample dry; LR is the moisture regain rate of the sample 'OR is the wet weight ratio of the sample, so
L=Gg/G (1)
R=g/G (2)
0R=(Gg)/G (3)
OR=G/g (4)
Test Purpose: Moisture content is an important factor affecting the processing of resins such as polyamide (PA) and polycarbonate (PC), product appearance and product characteristics. In the injection molding process, if plastic particles with too much moisture content are used for production, some processing problems will occur, which will ultimately affect the quality of the finished product, such as surface cracking, reflection, and mechanical properties such as impact resistance and tensile strength. .
3. Melt index test

Melting instrument
Melt Index: A value indicating the fluidity of a plastic material during processing.
Test method: first let the plastic pellets melt into a plastic fluid under a certain time (10 minutes), a certain temperature and pressure (different materials standards), and then pass through a diameter or volume of a diameter tube. The representation method is MFI: fluid mass; MVR: fluid volume.
Meaning: Indicates the processing fluidity of the plastic material. The larger the value, the better the fluidity, and vice versa. On the microscopic level, the larger the melting index, the smaller the viscosity and the smaller the molecular weight, and vice versa. The greater the viscosity of the plastic and the greater the molecular weight.
4, tensile / bending test
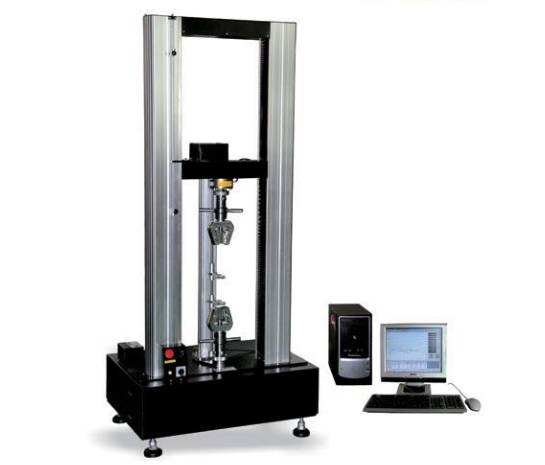

Bending/stretching tester
Tensile test: The basic physical properties of the polymer material are measured. After stress is applied to the material, the amount of deformation is measured, and the stress is obtained. The stress-strain curve is the most common method. Fix the ends of the spline with the appliance and apply the tensile load in the axial direction until the stress and distortion are destroyed.
Elastic modulus: E = (F / S) / (dL / L) (the material in the elastic deformation stage, its stress should be proportional to the relationship) elastic modulus" is a physical quantity describing the elasticity of the material, is a general term, including "Young's modulus", "shear modulus", "volume modulus", and the like.
The meaning of elastic modulus: elastic modulus is an important performance parameter of engineering materials. From a macroscopic point of view, elastic modulus is a measure of the ability of an object to resist elastic deformation. From a microscopic point of view, it is an atom, ion or molecule. The reaction between bond strengths.
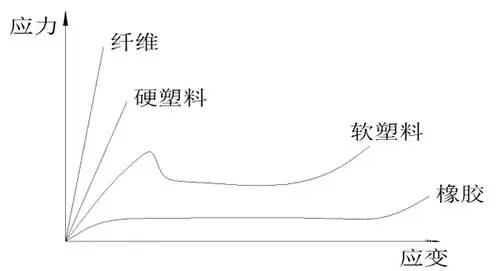
Different plastic tensile pattern changes
Strength: The maximum ability of a material to resist plastic deformation or damage under load.
Yield strength: The resistance of a material to significant plastic deformation.
Tensile strength: The maximum tensile stress experienced by a specimen until it breaks during the tensile test.
Tensile stress: The tensile load of the specimen on the initial cross section of the specimen within the gauge length range.
Tensile fracture stress: Stress at break on the σt-εt curve.
Tensile yield stress: The stress at the yield point on the σt-εt curve.
Elongation at break: The ratio of the increase in the distance between the lines to the initial gauge length when the sample is broken.
Yield point: The initial point at which σt does not increase with εt on the σt-εt curve.
Note:
The larger E is, the harder the material is, and the softer it is;
The larger σb or σy, the stronger the material, and the weaker the opposite;
The larger εb or S, the more tough the material, and the more fragile it is.
Factors affecting tensile properties
(1) Molding conditions: caused by microscopic defects and microscopic differences of the sample itself;
(2) temperature and humidity;
(3) Stretching speed: plastic is a viscoelastic material, and its stress relaxation process is closely related to the deformation rate, requiring a time process;
(4) Pretreatment: During the processing, due to the different time and speed of heating and cooling, local stress concentration is easy to occur. After heat treatment or annealing treatment at a certain temperature, internal stress can be eliminated and strength can be improved.
(5) Material properties: crystallinity, orientation, molecular weight and distribution, degree of crosslinking;
(6) Aging: The strength is significantly reduced after aging.
Bending performance test: The bending test is performed by placing the spline on two fulcrums of a certain length and bending at a certain speed when applying a load at the intermediate portion until the stress is twisted when causing the break or reaching a certain amount of bending. .
Flexural Strength: The force applied at the center of the spline at a certain speed, the spline breaks or the strength at which the 5% deformation is reached. The bending strength is a test for the resistance when the spline is deformed to cause deformation.
Flexural Modulus: refers to the ratio of the amount of force applied from the upper portion of the center of the spline to the deformation produced by the spline. The greater the flexural modulus, the stronger the rigidity, and the smaller the flexural modulus, the softer the plastic.

Bending test
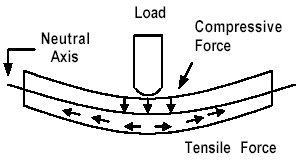
Spline bending deformation
5, impact test

Impact tester
Definition: The pendulum strikes the middle of the specimen of the simply supported beam, causing the specimen to be impacted and fractured. The impact energy consumed per unit area or unit width when the specimen breaks is the impact strength.
Significance: Impact toughness is a description of the toughness or fracture resistance of polymer materials under high-speed impact. In general, impact toughness includes two aspects: the ability to deform after impact and the ability to break the crucible. The former is generally expressed by the elongation at break, while the latter is generally expressed by the impact strength.
Impact strength calculation formula: E=A/bd
A: indicates the work consumed during the impulse; b/d indicates the width and thickness of the impacted portion; E is the impact strength.
The work consumed to break the sample is generally divided into the following aspects:
a) crack causing the sample to crack
b) disconnect some of the cracks throughout the sample
c) deforming the polymer near the crack
d) fly off the broken sample fragments
e) a small amount of overcoming air resistance and friction between mechanical parts
Note: In general, the greater the impact energy absorbed before being destroyed, the greater the elongation at break, and the better the impact toughness of the material.
6, heat distortion temperature test
Heat deflection temperature: A temperature applied to a polymer material or polymer to increase the temperature at a certain speed when the specified deformation is reached.
Test principle: The plastic sample is placed on a support with a span of 100 mm, placed in a suitable liquid heat transfer medium, and a specific static bending load is applied to the midpoint of the two seats. Under the condition of constant temperature rise, the bending deformation of the sample reaches the specified value.
Test purpose: high-polymer in glass or crystalline state, with the increase of temperature, the energy of atomic and molecular motion increases, and the ability to deform due to its directional motion under external force increases, that is, the ability of the material to resist external forces - The modulus decreases with increasing temperature, and as the temperature increases, the deformation of the plastic increases under a fixed load.
Influencing factors:
1) Test instrument (reading error, sample placement position)
2) Method and size of sample preparation
3) Heat transfer medium
7, Vicat softening temperature test
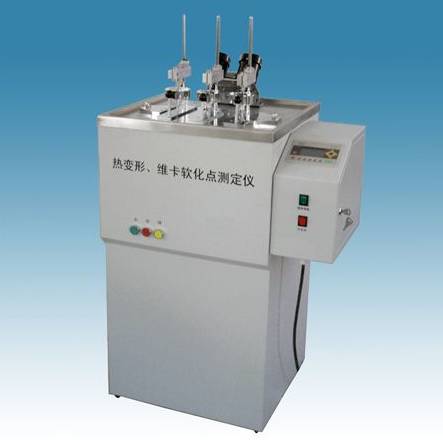

Vicat tester
Test principle: The plastic spline is placed in a liquid heat transfer medium. Under a certain load and a certain constant temperature temperature rise condition, the sample is pressed into the temperature of 1 mm by a 1 mm square pressure needle.
Significance: Vicat softening temperature is one of the indicators to evaluate the heat resistance of materials and reflect the physical and mechanical properties of products under heat. The Vicat softening temperature of the material cannot be directly used to evaluate the actual use temperature of the material, but can be used to guide the quality control of the material. The higher the Vicat softening temperature, the better the dimensional stability of the material when heated, and the smaller the thermal deformation, that is, the better the heat deformation resistance, the greater the rigidity and the higher the modulus.
8, heat aging test

Aging furnace
Test principle: The plastic sample is placed in a heat aging test chamber of a given condition (temperature, wind speed, air exchange rate, etc.) to be subjected to accelerated aging of heat and oxygen.
Objective: To test the change of performance before and after exposure and evaluate the heat aging resistance of plastics.
9, viscosity test

Viscosity tester
Plastic viscosity: refers to the coefficient of friction between macromolecules when the plastic melts. It is a reflection of the high fluidity of plastic melt, that is, the greater the viscosity, the stronger the melt viscosity, the worse the fluidity, the more difficult the processing, and also the evaluation method of the molecular weight of the polymer. The viscosity of the plastic is inversely proportional to the melt index of the plastic. The viscosity of the plastic varies with the characteristics of the plastic itself, external temperature, pressure and other conditions.
10
Combustion test
Combustion performance: refers to all physical and chemical changes that occur when a material burns in a fire. This property has the ignitability and flame spread of the material surface, heat, smoke, carbonization, weight loss, and the production of toxic products. measure.
Test methods: main aerobic index combustion performance test, horizontal combustion performance test, vertical combustion performance test, glow wire flammability index test. The flame retardant properties of the material directly affect the use of the material.
Test principle: Fix one end of the rectangular strip spline on the horizontal or vertical fixture, the other end is exposed to the specified test flame, and measure the horizontal burning behavior by measuring the linear burning rate; by measuring the rest of the fireworks and the remaining The burning time of the plastic was evaluated by the flame time, the burning range, and the low particle.
The meaning of the test: Under the specified conditions, the combustion properties of different materials are of great significance to the range of materials used, as well as the manufacturing process and the changing characteristics of combustion.
Solar Flood Light,LED Solar Flood Lights,Solar Powered Flood Lights,Solar LED Flood Lights
Ningbo Deamak Star Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.deamakstar.com